* This paper is the author’s personal view
Oil and gas extractive industry activities consist of upstream business activities and downstream business activities. Downstream business activities are based on exploration and exploitation activities, while downstream business activities are based on processing, storage and commercial activities1. Upstream business activities are carried out and controlled through Cooperation Contracts (KKS), while downstream business activities are carried out through business licenses. The development and supervision of upstream oil and gas business activities is carried out by BPMIGAS (the upstream oil and gas business executing agency), while the training and supervision of downstream oil and gas activities is carried out by the BPH Migas (the downstream oil and gas business executing agency)2. BPMIGAS has the legal status as a BHMN (state-owned legal entity).
Upstream and downstream oil and gas business activities can be carried out by State-Owned Enterprises (BUMN); Regionally Owned Enterprises (BUMD); Cooperatives, small businesses and private businesses. Business Entity (BU)3 or Permanent Establishment (BUT)4 that conducts upstream business activities is prohibited from conducting downstream business activities, and vice versa. If a business entity conducts upstream and downstream activities simultaneously, it must form a separate legal entity, including a holding company. BU and BUT must get permission from the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (cq. DG Oil and Gas).
The taxonomy of the national oil and gas business sector
Broadly speaking, the taxonomy of our national oil and gas business sector can be illustrated in the following chart:
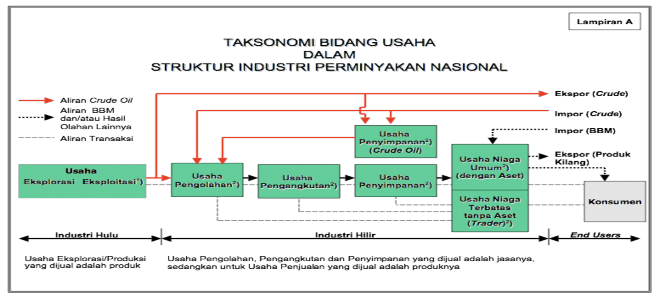
explanation of the picture: the national petroleum business sector generally consists of upstream businesses, downstream businesses up to the end users. The upstream industry consists of exploration and exploitation (production) businesses that produce products in the form of crude oil (crude oil flow is depicted with red arrows). Crude oil is directly exported and some is used to meet domestic needs, which is included in the downstream industry which includes processing, transportation, storage, to commercial businesses both general and limited (without assets). From the commercial business, fuel oil (BBM) or other processed products are produced which reach the consumers (end users). Some of the fuel to meet the needs of domestic consumers is also imported from abroad and vice versa there are also processed products that are exported. In every chain of activities, from upstream, downstream to trade to consumers, there is a flow of financial transactions.
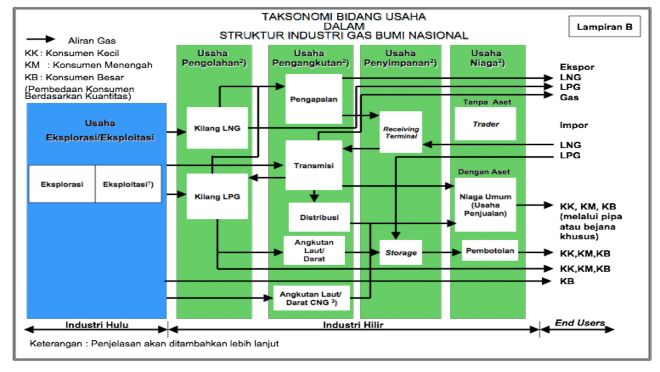
explanation of the picture: the national natural gas business sector in general consists of upstream businesses, downstream businesses up to the end users. The upstream industry consists of exploration and exploitation (production) businesses that produce natural gas products (natural gas flows are depicted with black arrows). The natural gas enters the downstream industry which includes: processing gas into LNG and LPG, then entering the transportation business, namely shipping for export, transportation to transmission, distribution by land or sea transportation. The transportation is directed to the storage business as well as to the commercial business to reach consumers (end users) consisting of KK (small consumers), KM (medium consumers), and KB (large consumers). In fact, since the upstream industry, there has also been direct sales of natural gas to KB (large consumers) and after becoming LPN and LNG there is also trade directly to KK, KM, and KB.
Footnotes
- 1Oil and Gas Law No.22 / 2001, Article 5
- 2Ibid, article 11, article 23 and article 44
- 3Business Entity (BU) is a company in the form of a legal entity that operates a permanent, continuous and established type of business in accordance with applicable laws and regulations and works and is domiciled in the territory of the Unitary State of the Republic of Indonesia (article 1 number 17, Law No.22 / 2001 about Oil and Gas)
- 4Permanent Business Establishments are business entities established and incorporated outside the territory of the Unitary State of the Republic of Indonesia that carry out activities in the territory of the Unitary State of the Republic of Indonesia and are required to comply with the laws and regulations in force in the Republic of Indonesia (article 1 number 18, Law No.22 / 2001 concerning Oil and Gas)